Price improvement (PI) occurs when your orders are executed at better prices than the best quoted market price, known as the National Best Bid and Offer, or more commonly, NBBO. This price difference saves you money.
To better understand price improvement, you must first understand the National Best Bid and Offer (NBBO), the quote disseminated market wide to investors. Under SEC rules, the NBBO consists of the highest displayed buy and lowest sell prices among the various exchanges trading a security. Exchanges and liquidity providers can route orders to the exchange with the best quote represented in the NBBO, or alternatively, can match or improve those prices and execute on their own market venue.
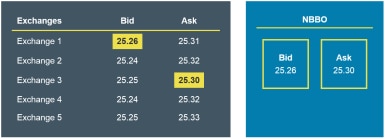
Let’s look at quotes from various exchanges on shares of XYZ stock.

The highest buying price (Bid) and the lowest asking price (Ask) is the NBBO.
In the equity markets, all available liquidity may not be displayed in the NBBO. Market participants may choose not to display their orders to avoid revealing their trading interest. To accommodate those traders, securities exchanges and ATSs allow them to post their orders anonymously and not publicly visible ("dark"), away from the publicly displayed ("lit") quotes. Accessing this better-priced non-displayed liquidity creates opportunities for liquidity providers to improve your executions. In addition, when executing orders as a market maker, a liquidity provider is often willing to trade at better prices than the NBBO.
Price improvement on an individual transaction is determined based upon the difference between the execution price and the NBBO at the time your marketable order is routed. The amount of price improvement per share may be less than the minimum quotation price increment (typically, one cent).
For example, say you place an order to buy 1,000 shares of XYZ stock currently quoted at $25.30 per share. If your order is executed at $25.29, then you realize $0.01 per share of price improvement, resulting in a total savings of $10.00 (1,000 shares × $0.01).

To find out the percentage of orders that have received price improvement and the average improvement amounts over the last quarter, visit our Retail Execution Quality Statistics page.
Another way that liquidity providers may price improve orders when trading as market maker is to match the NBBO price for more shares than the displayed size available at the NBBO. This is often referred to as liquidity enhancement.
For example, an order is placed to buy 1,000 shares of XYZ stock currently quoted at $25.30, and the NBBO reflects that only 500 shares are available at that price. If the order were routed to the market venue showing those 500 shares for sale, the entire order may not be filled. Liquidity enhancement occurs when a liquidity provider honors the NBBO price and fills the additional 500 shares at $25.30.

Schwab is committed to putting your interests first and to transparency in our order routing practices and execution quality performance.
Learn about Schwab Order Execution Advantage™ See how order routing worksAn Alternative Trading System (ATS) is an execution platform that brings together buyers and sellers of securities, similar to how orders are matched on an exchange. The system operator must be a licensed broker-dealer registered under SEC Rule ATS and must comply with various conduct and reporting requirements.
Liquidity providers are broker-dealers who execute orders based on their assessment of how to obtain the best executions. They may act as market makers and execute orders against their own account or route orders directly to other execution venues such as Alternate Trading Systems or securities exchanges.
A market maker commits its own capital and stands prepared to buy and sell securities during the trading day at quoted prices.
National Best Bid and Offer (NBBO)
National Best Bid and Offer (NBBO) represents the highest displayed bid price and lowest displayed offer price available for a security across the various exchanges or liquidity providers. Exchanges, ATSs, and liquidity providers are generally required by the Order Protection Rule (SEC Reg NMS Rule 611) to execute orders at the best displayed price or better.
A securities exchange is an entity that has registered with the SEC under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 and facilitates the buying and selling of securities among market participants.
System availability and response times are subject to market conditions and mobile connection limitations.